Introduction
The goal of this Field Methods lab activity was to familiarize us with the various spatial analysis tools that are commonly used on DEM raster files in ArcGIS desktop applications. Understanding what each of these common tools does and the products that will be created upon running these tools was also an important goal of this lab. Finally, another goal was to gain experience in the viewing of DEM raster data in a 3D platform such as ArcScene
Methods
To begin this lab, provided DEM data was copied into our individual class folders. This data, had it not been provided for us, was obtainable through the WI DNR or through the USGS. With this data, we opened ArcGIS desktop and created a file geodatabase to house the data in each of our individual folders. With this done, the final step before processing the data was to turn on the Spatial Analyst extension under the Customize menu to allow for the use of Spatial Analyst tools.
With these set up steps complete, the first tool to be run was the Contour Tool found under Spatial Analyst>Surface>Contour. This too creates contour lines at a user set interval, in this case 10 meters, and exports the output as a layer that can be added to a map document.
Figure 1. 10 meter contour interval of Eau Claire County DEM
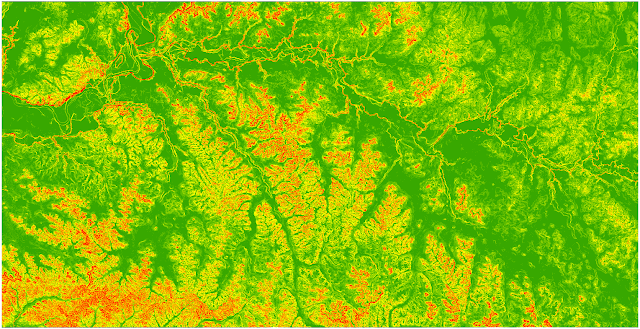
The next Spatial Analysis tool to be run was the slope tool, found under Spatial Analyst>Surface>Slope. This tool creates a raster file showing the relative steepness of slopes based off an input DEM.
Figure 2. Slopes of Eau Claire County DEM
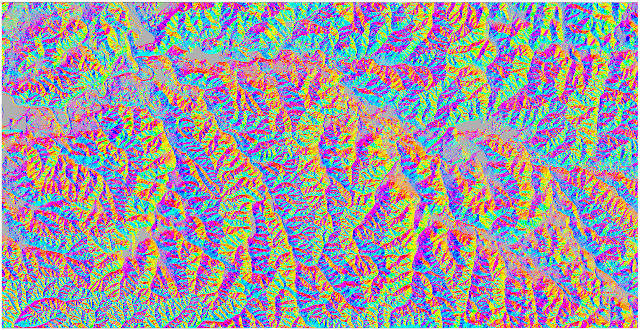
The next tool after slope was the aspect tool, found under found under Spatial Analyst>Surface>Aspect. This tool determines the aspect, or the cardinal direction, that each slope faces.
Figure 3. Slope Aspect of Eau Claire County DEM
The final Spatial Analysis tool to be run on this DEM is the Hillshade tool, found under Spatial Analyst>Surface>Hillshade. This tool creates a shaded relief of a DEM that allows for better visualization of the topography of an area.
Figure 4. Hillshade of Eau Claire County DEM
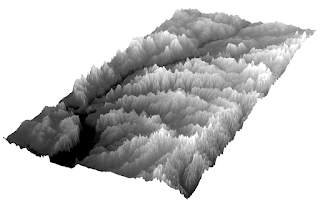
Once all of the Spatial Analysis tools had been run, the next step was to visualize the DEM in ArcScene. This was done to express the DEM in all three dimensions rather than in 2D like in ArcGIS desktop. To do this, the DEM was set to 'floating on a custom surface' either by meters to feet, feet to meters, or based on a custom value. These values determined the overall vertical exaggeration of the DEM.
Figure 5. Eau Claire County DEM shown with different levels of vertical exaggeration.
Discussion
This lab was very straight forward, with simple easy to understand directions that guided us students through the lab to accomplish the goals of the exercise.
Conclusion
Overall this lab was very useful in developing my understanding of some of the spatial analyst tools present in ArcGIS desktop. this lab was also great in allowing us to gain more experience in working with DEM's both in ArcGIS desktop and ArcScene as well.
Evaluation
Evaluation
1. Prior
to this activity, how would you rank yourself in knowledge about the topic.
4-A good amount of knowledge
2.
Following
this activity, how would you rate the amount of knowledge you have on the topic
5- I am an expert)
3.
Did
the hands-on approach to this activity add to how much you were able to learn.
4-Agree
4.
What
types of learning strategies would you recommend to make the activity even
better?
More in depth use of these spatial tools for a wider variety of applications.